-
Installation
-
With Kamon Telemetry
-
How To Guides
-
Migrations
-
-
Core Concepts
-
Foundations
-
Advanced
-
-
Instrumentation
-
Supported Frameworks
-
Akka
-
Akka HTTP
-
Cassandra Driver
-
Caffeine
-
Elasticsearch
-
Executors
-
Futures
-
JDBC
-
Kafka
-
Logback
-
Play Framework
-
Spring Framework
-
System Metrics
-
-
-
Reporters
-
Kamon APM
-
Using Kamon APM
-
Overview
-
Services
-
Traces
-
Dashboards
-
Alerts
-
Hosts
-
Investigating Issues
-
Settings and Administration
-
-
Instrumentation Agent Setup #
In most situations, you won’t need to do anything special to set up the Kanela agent other than following the instructions
in the Installation Guides. In a guided installation either the call to Kamon.init() or the SBT
plugins will take care of attaching the Kanela agent at runtime.
Nevertheless, sometimes things get weird and you need alternative options. This how to summarizes all the ways in which you could start your applications with the Kanela agent. Let’s get to it!
In a Nutshell #
All you need to do is download the latest release from our Kanela releases
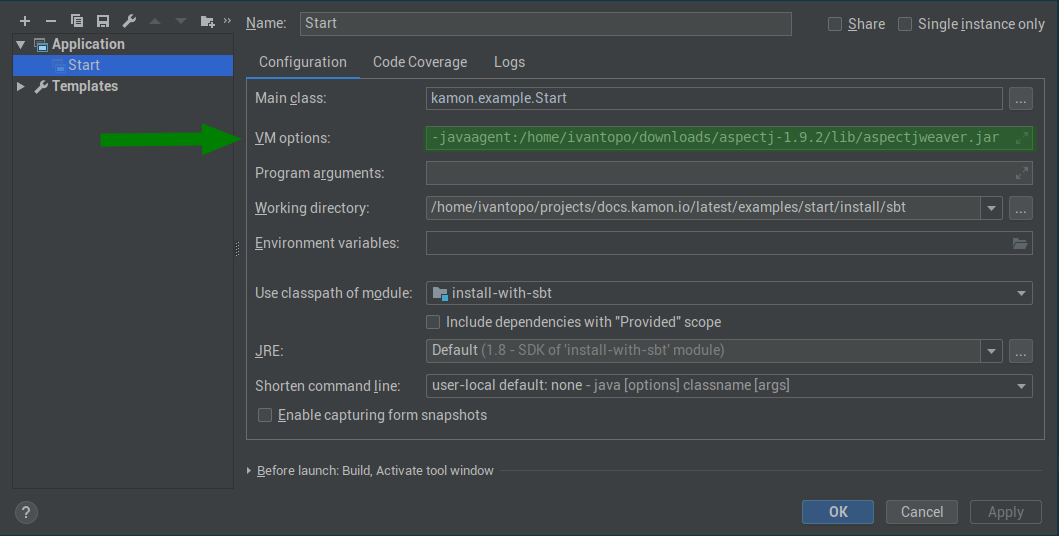
repository and start your JVM with the -javaagent:path-to-kanela.jar JVM option. For example, if you are running your
application from IntelliJ IDEA you will need to add the -javaagent option to the “VM options” section as shown below:
And that is pretty much it. Even though it is a simple task, it can be challenging in different environments so please, follow the instructions below when:
- Running applications from SBT
- Running a Play Framework application on development mode
- Packaging applications with sbt-native-packager
Running from SBT #
The simplest solution is to use the sbt-kanela-runner plugin. This
plugin will ensure that the instrumentation is applied to your classes regardless of whether you are forking the process
(via fork in run := true) or not. To get it working add these lines to your project/plugins.sbt file:
addSbtPlugin("io.kamon" % "sbt-kanela-runner" % "2.0.14")That’s it! Next time your application starts, instrumentation will be enabled.
Play Framework #
Once again, the sbt-kanela-runner plugin is the way to go. The plugin has special variants for Play applications that will have special treatment of Play’s infrastructure for running on Development mode, to include it you must add the right plugin depending on your Play version:
Play 2.8 #
// For Play Framework 2.8.8
addSbtPlugin("io.kamon" % "sbt-kanela-runner-play-2.8" % "2.0.14")
// OR for Play Framework <= 2.8.7
addSbtPlugin("io.kamon" % "sbt-kanela-runner-play-2.8" % "2.0.10")Play 2.7 #
addSbtPlugin("io.kamon" % "sbt-kanela-runner-play-2.7" % "2.0.14")Play 2.6 #
addSbtPlugin("io.kamon" % "sbt-kanela-runner-play-2.6" % "2.0.14")The runner brings the sbt-javaagent dependency with it, but it requires
you to active it explicitly by calling .enablePlugin(JavaAgent) on the right project instance in your build.sbt file,
it should look like this:
Using sbt-native-packager #
You can use the sbt-javaagent plugin together with sbt-native-packager
to get the Kanela agent option automatically added to the startup scripts. To achieve this, first add the plugin to your
project/plugins.sbt file:
addSbtPlugin("com.lightbend.sbt" % "sbt-javaagent" % "0.1.6")And enable the plugin in your build.sbt file:
lazy val root = (project in file("."))
.enablePlugins(JavaAppPackaging, JavaAgent)
javaAgents += "io.kamon" % "kanela-agent" % "1.0.16"You can find additional details on the sbt-javaagent GitHub repo.