You are viewing documentation for an outdated version. Do you wish to see documentation for the latest version?
Instrumentation Agent Setup #
All you need to do is download the latest stable release from the official website and start your JVM
with the -javaagent:path-to-aspectjweaver.jar JVM option. For example, if you are running your application from
IntelliJ IDEA you will need to add the -javaagent option to the “VM options” section as shown below:
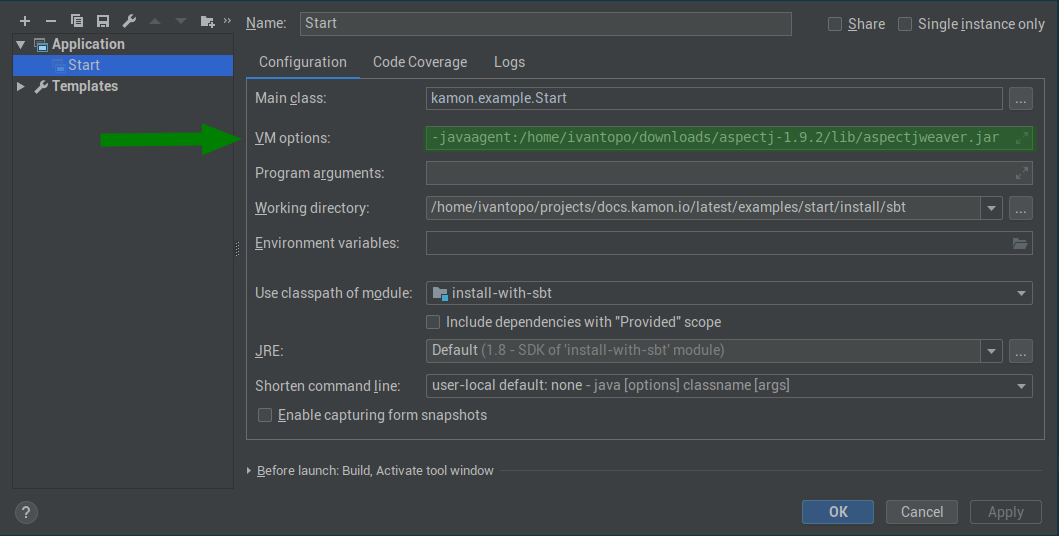
And that is pretty much it. Even though it is a simple task, it can be challenging in different environments so please, follow the instructions below when:
- Running applications from SBT
- Running a Play Framework application on development mode
- Packaging applications with sbt-assembly
- Packaging applications with sbt-native-packager
Plain SBT #
The simplest solution is to use the sbt-aspectj-runner plugin. This plugin will ensure that the
instrumentation is applied to your classes regardless of whether you are forking the process (via fork in run := true)
or not. To get it working add these lines to your project/plugins.sbt file:
resolvers += Resolver.bintrayIvyRepo("kamon-io", "sbt-plugins")
addSbtPlugin("io.kamon" % "sbt-aspectj-runner" % "1.1.2")That’s it! You can visit the GitHub repo for additional details on how the plugin works.
Play Framework #
Once again, the sbt-aspectj-runner is the way to go. The plugin has special variants for Play applications that will have special treatment of Play’s infrastructure for running on Development mode, to include it you must add the right plugin depending on your Play version:
Play 2.7 #
resolvers += Resolver.bintrayIvyRepo("kamon-io", "sbt-plugins")
addSbtPlugin("io.kamon" % "sbt-aspectj-runner-play-2.7" % "1.1.2")Play 2.6 #
resolvers += Resolver.bintrayIvyRepo("kamon-io", "sbt-plugins")
addSbtPlugin("io.kamon" % "sbt-aspectj-runner-play-2.6" % "1.1.2")Play 2.4 and 2.5 #
resolvers += Resolver.bintrayIvyRepo("kamon-io", "sbt-plugins")
addSbtPlugin("io.kamon" % "sbt-aspectj-play-runner" % "1.0.4")Using sbt-assembly #
Since sbt-assembly puts your entire classpath in a single jar, it needs to merge files that have the same path across
several jars and that includes the META-INF/aop.xml files that ship in all the instrumentation modules. The default
merge strategy will resolve the conflict by picking the first file found in the classpath and even though that would
generate a jar with all the instrumentation, you will notice that some instrumentation is working and some is missing,
depending on which aop.xml file was picked.
Cool thing is, there is a custom merge strategy that takes care of merging these files. This is how it looks like:
// Create a new MergeStrategy for aop.xml files
val aopMerge: MergeStrategy = new MergeStrategy {
val name = "aopMerge"
import scala.xml._
import scala.xml.dtd._
def apply(tempDir: File, path: String, files: Seq[File]): Either[String, Seq[(File, String)]] = {
val dt = DocType("aspectj", PublicID("-//AspectJ//DTD//EN", "http://www.eclipse.org/aspectj/dtd/aspectj.dtd"), Nil)
val file = MergeStrategy.createMergeTarget(tempDir, path)
val xmls: Seq[Elem] = files.map(XML.loadFile)
val aspectsChildren: Seq[Node] = xmls.flatMap(_ \\ "aspectj" \ "aspects" \ "_")
val weaverChildren: Seq[Node] = xmls.flatMap(_ \\ "aspectj" \ "weaver" \ "_")
val options: String = xmls.map(x => (x \\ "aspectj" \ "weaver" \ "@options").text).mkString(" ").trim
val weaverAttr = if (options.isEmpty) Null else new UnprefixedAttribute("options", options, Null)
val aspects = new Elem(null, "aspects", Null, TopScope, false, aspectsChildren: _*)
val weaver = new Elem(null, "weaver", weaverAttr, TopScope, false, weaverChildren: _*)
val aspectj = new Elem(null, "aspectj", Null, TopScope, false, aspects, weaver)
XML.save(file.toString, aspectj, "UTF-8", xmlDecl = false, dt)
IO.append(file, IO.Newline.getBytes(IO.defaultCharset))
Right(Seq(file -> path))
}
}
// Use defaultMergeStrategy with a case for aop.xml
// I like this better than the inline version mentioned in assembly's README
val customMergeStrategy: String => MergeStrategy = {
case PathList("META-INF", "aop.xml") =>
aopMerge
case s =>
defaultMergeStrategy(s)
}
// Use the customMergeStrategy in your settings
mergeStrategy in assembly := customMergeStrategyYou might need to integrate this slightly different in your build if you have other merge strategy configurations. Then
the fat jar can be ran as usual with the -javaagent:path-to-weaver.jar option.
Using sbt-native-packager #
You can use the sbt-javaagent plugin together with sbt-native-packager to get the AspectJ Weaver
option automatically added to the startup scripts. To achieve this, first add the plugin to your project/plugins.sbt
file:
addSbtPlugin("com.lightbend.sbt" % "sbt-javaagent" % "0.1.4")And enable the plugin in your build.sbt file:
lazy val root = (project in file("."))
.enablePlugins(JavaAppPackaging, JavaAgent) // (1)
javaAgents += "org.aspectj" % "aspectjweaver" % "1.9.2" // (2)
javaOptions in Universal += "-Dorg.aspectj.tracing.factory=default" // (3)A few comments from the above:
- You need to enable the
JavaAgentplugin in your project. - This line defines the AspectJ Weaver dependency, always try to use the latest stable version.
- This additional settings helps get less “false errors” from the AspectJ Weaver which are usually confused with real errors.
You can find additional details on the sbt-javaagent GitHub repo.