You are viewing documentation for an outdated version. Do you wish to see documentation for the latest version?
Configuring Kamon #
Kamon uses the Typesafe Config library to manage all that can be configured inside Kamon, as many projects in the JVM world are doing already. This library brings clear and predictable practices for defining application and library settings that can be easily understood and extended. If you are already familiar with this library, you can just jump into the next section.
The Typesafe Config’s standard behavior is very straightforward and we will resume it for you: When you create a
configuration object using ConfigFactory.load(), it will read the available configurations from a few predefined
places and have them ready for you, so that whenever you want to read a configuration setting they will be looked up
in the following order:
- JVM System Properties.
- All
application.conffiles in your classpath. - All
application.jsonfiles in your classpath. - All
application.propertiesfiles in your classpath. - All
reference.conffiles in your classpath.
Normally, each library that uses the Typesafe Config library for configuration purposes will ship with a
reference.conf file containing sensible default values for all the settings that can be configured and the user will
provide “overrides” to those values primarily via your own application.conf file or via system properties. Probably an
image of the common lookup priorities will settle quickly in your mind:
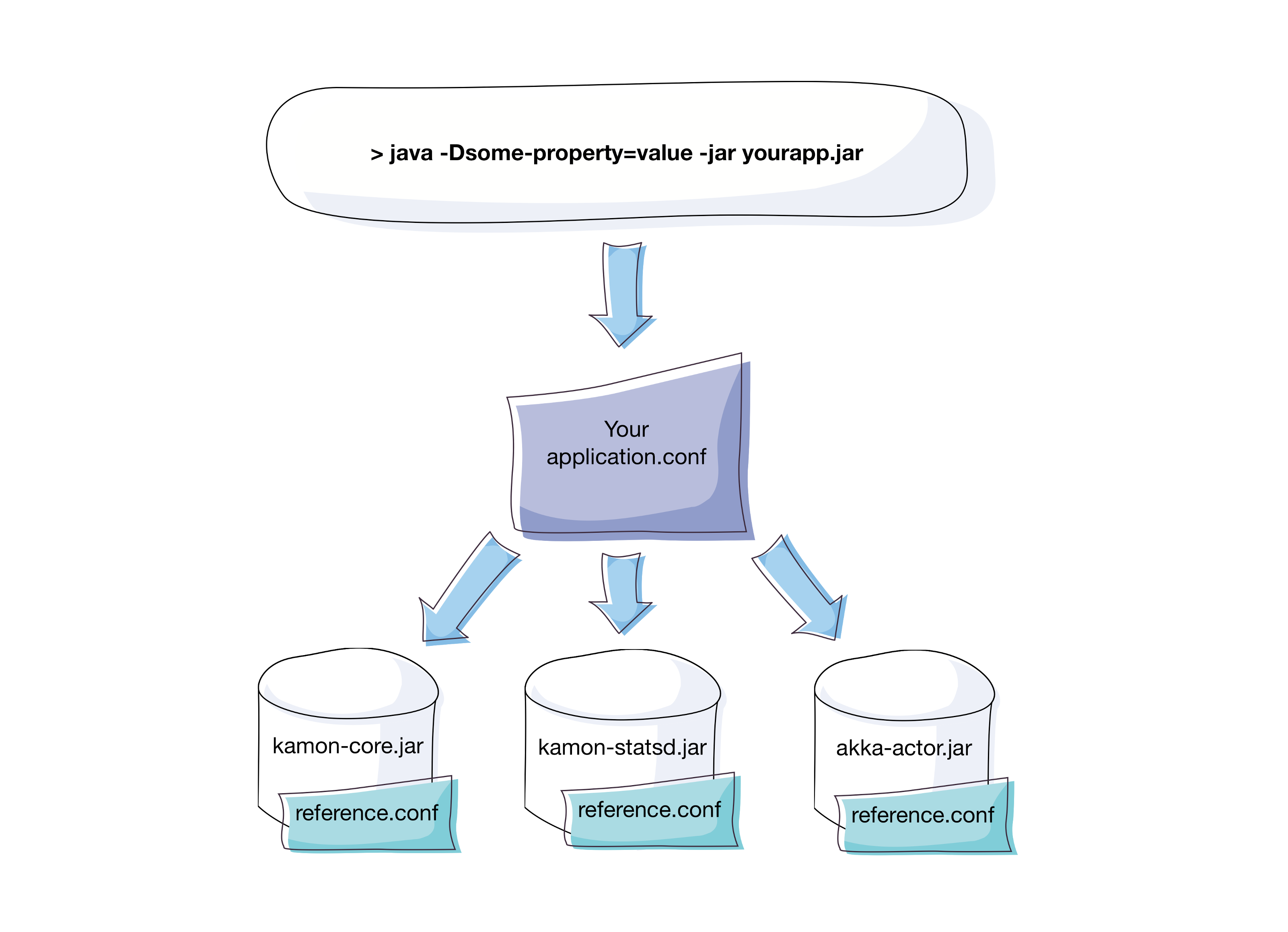
These configuration files are usually written using the HOCON notation. All Kamon modules that need configuration ship
with a reference.conf file where default settings are contained and you are free to override any of those values by
supplying your owns in your application.conf file. Whenever we refer to a configuration setting throughout the docs,
we are certainly referring to a setting available in a module’s reference.conf file that you can override at your
wish.
This resume is just a very high level overview of what the Typesafe Config library can do for you, please refer to their documentation to learn how to slice and dice with configuration settings and make the best possible profit out of it.
Providing a Custom Config Object #
If you need to supply Kamon with a custom configuration object, call the Kamon.reconfigure(..) method that with your
new configuration object.
object CustomConfiguration extends App {
val customConfig = ConfigFactory.load("custom-config")
val codeConfig = ConfigFactory.parseString("kamon.metric.tick-interval = 15 seconds")
// Kamon gets reconfigured with the provided configuration.
Kamon.reconfigure(codeConfig.withFallback(customConfig))
}Please note that when you provide your own Config object, Kamon will use that and only that object as a configuration
settings source. You must ensure that the Config object you are supplying contains both your custom settings and all
the reference settings available in the classpath. Most APIs in the typesafe-config’s ConfigFactory class already take
care of that but if that isn’t the case for you then simply adding a .withFallback(ConfigFactory.defaultReference())
to your configuration object you can ensure that everything Kamon needs is in place.